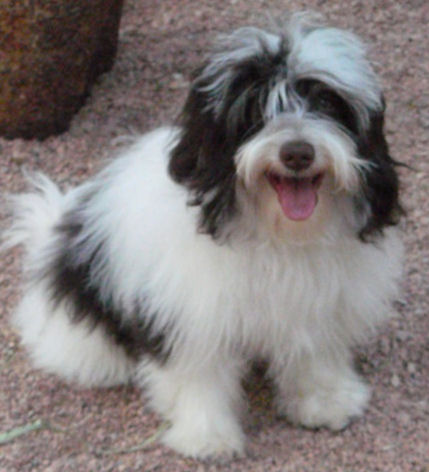
What
is a chocolate colored Havanese ?
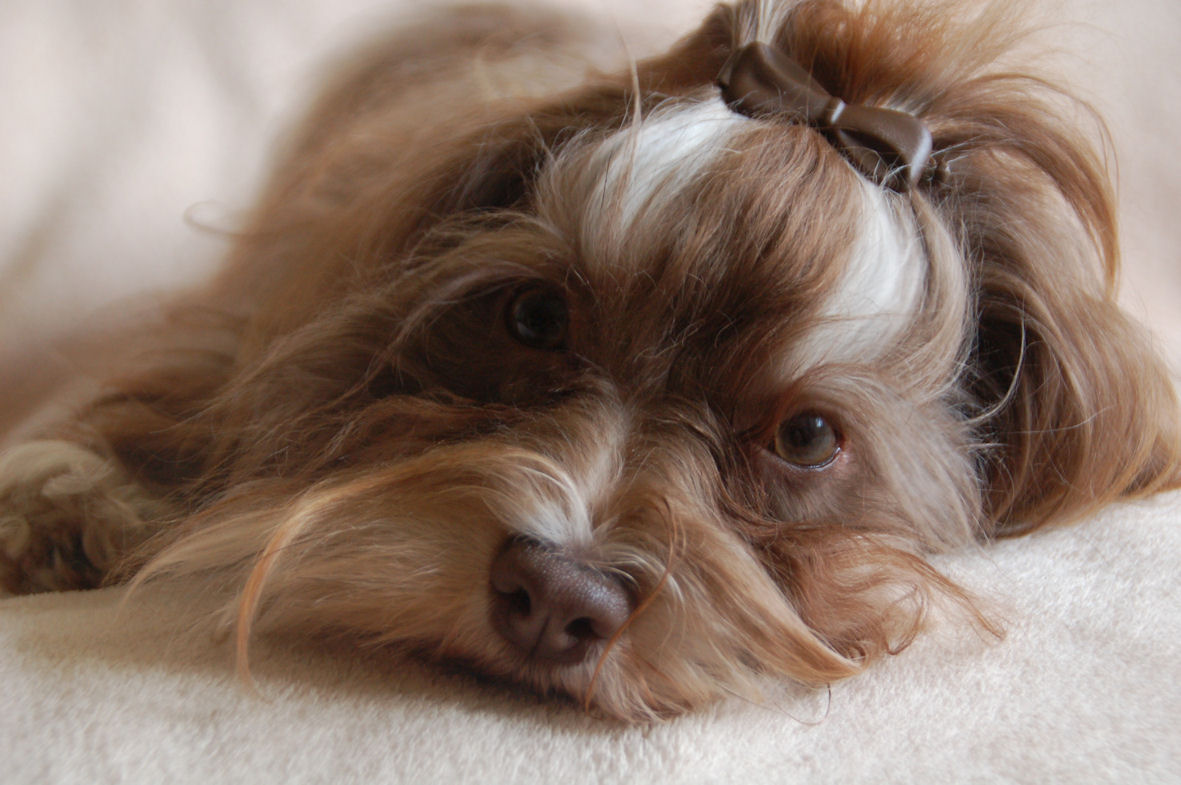
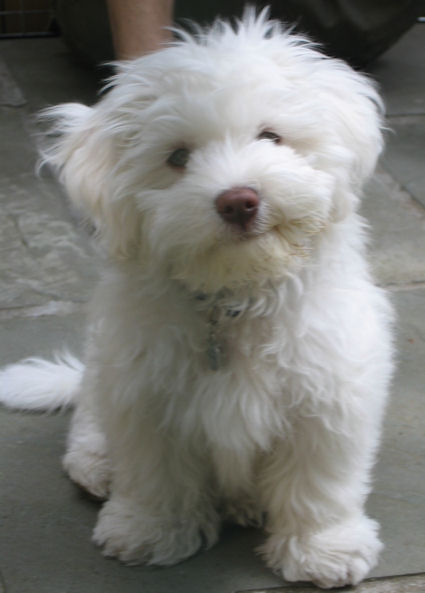
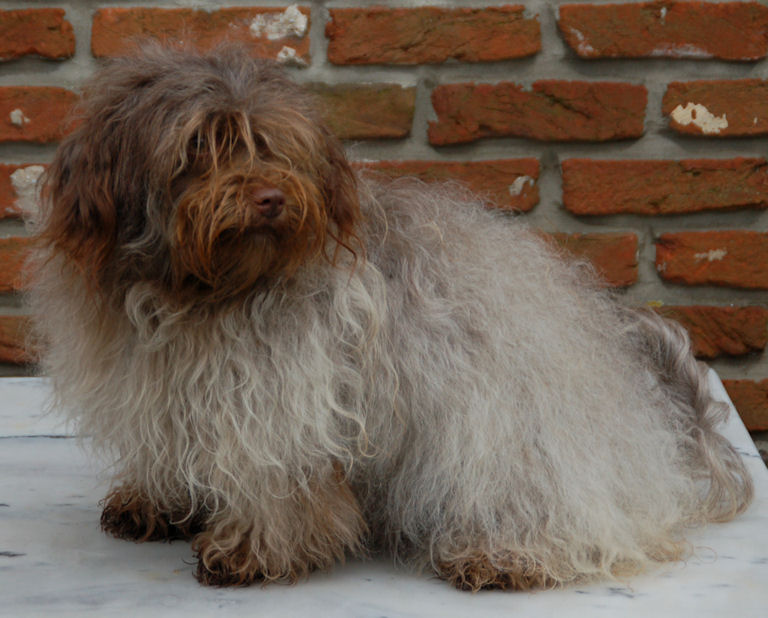
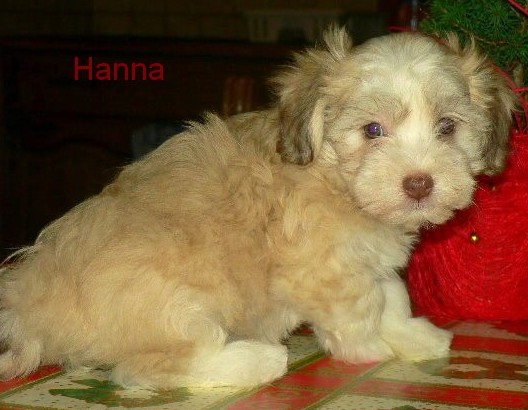
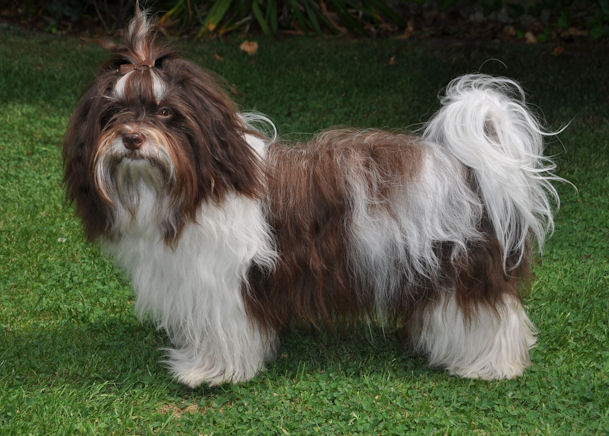
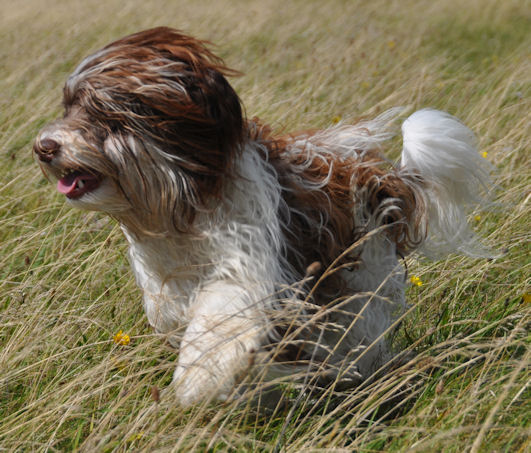
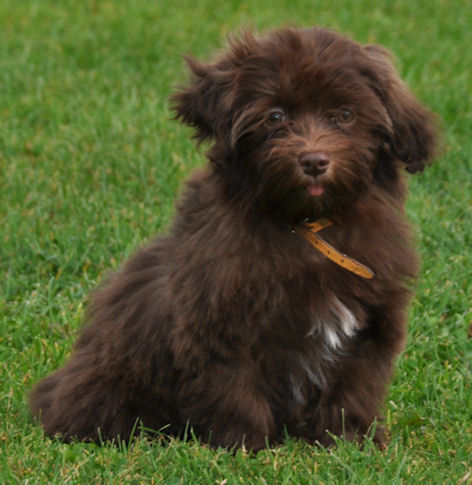
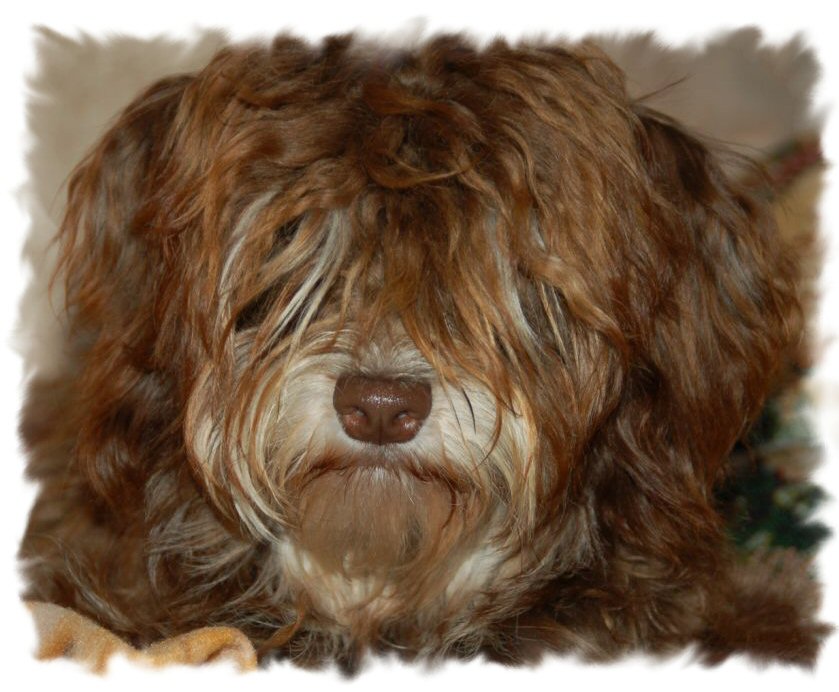 A
chocolate coloured Havanese is a dog with a
chocolate or liver coloured coat AND with a
brown nose, brown eyelids, brown lips and brown
soles! A chocolate coloured Havanese can not
have any black pigment
(photo on the right)! A
chocolate Havanese has brown, hazelnut or amber
eyes. These dogs have the brown or liver pigment
[bb]. The
Havanese with a chocolate coat can't have any
black hair nor black pigment. A
chocolate coloured Havanese is a dog with a
chocolate or liver coloured coat AND with a
brown nose, brown eyelids, brown lips and brown
soles! A chocolate coloured Havanese can not
have any black pigment
(photo on the right)! A
chocolate Havanese has brown, hazelnut or amber
eyes. These dogs have the brown or liver pigment
[bb]. The
Havanese with a chocolate coat can't have any
black hair nor black pigment.
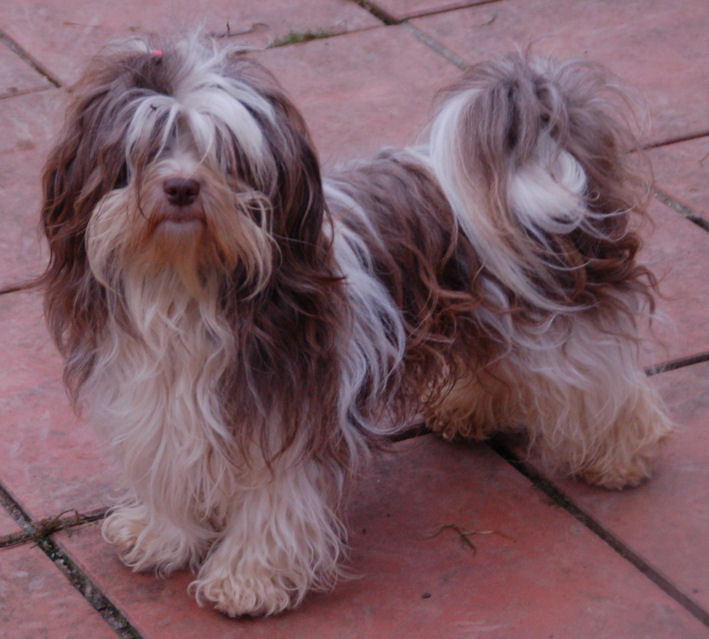
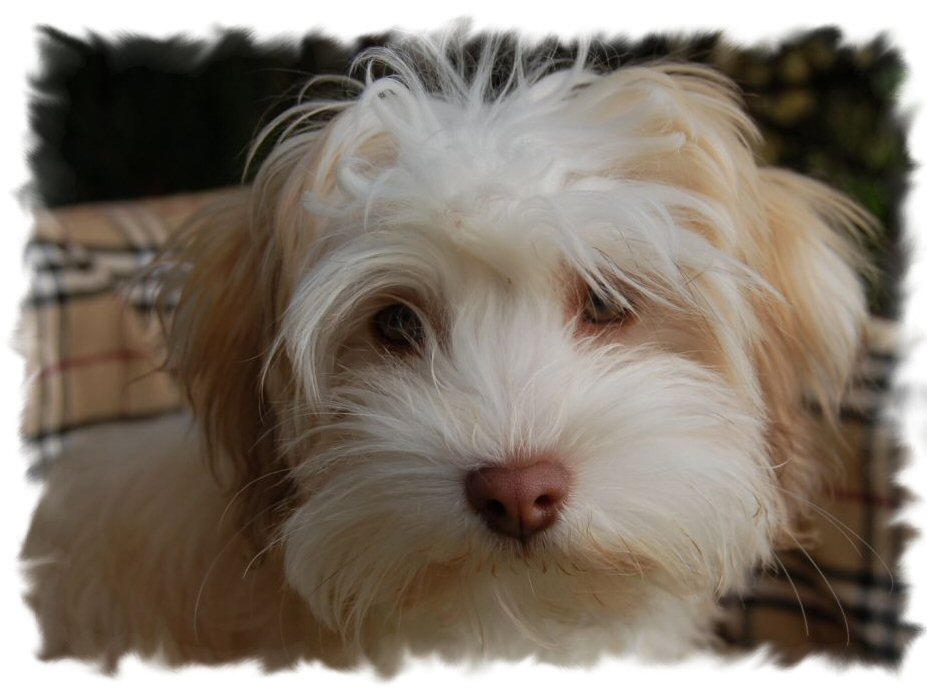 The
brown / chocolate coat can vary from milk
chocolate to dark chocolate and they can appear
in the same variations, markings and patterns as
the black pigmented dogs. Chocolate Sable,
Chocolate Brindle and Chocolate & Tan
Havanese exist, but also Chocolate Irish Pied,
Chocolate Parti and (Extreme) Piebald. The
brown / chocolate coat can vary from milk
chocolate to dark chocolate and they can appear
in the same variations, markings and patterns as
the black pigmented dogs. Chocolate Sable,
Chocolate Brindle and Chocolate & Tan
Havanese exist, but also Chocolate Irish Pied,
Chocolate Parti and (Extreme) Piebald.
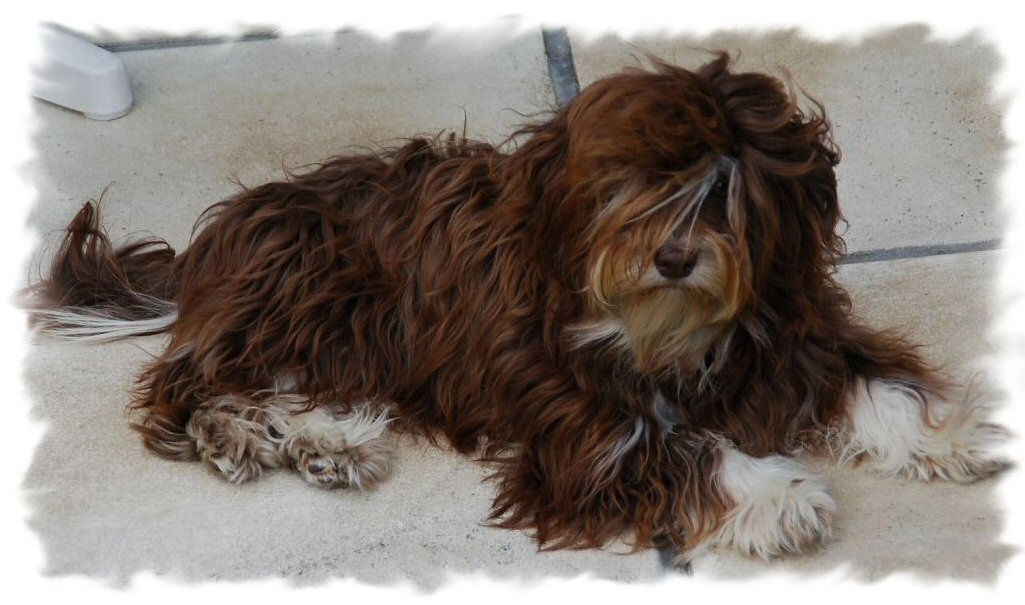
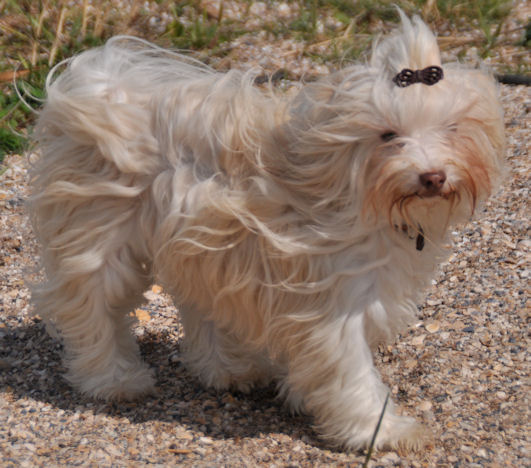
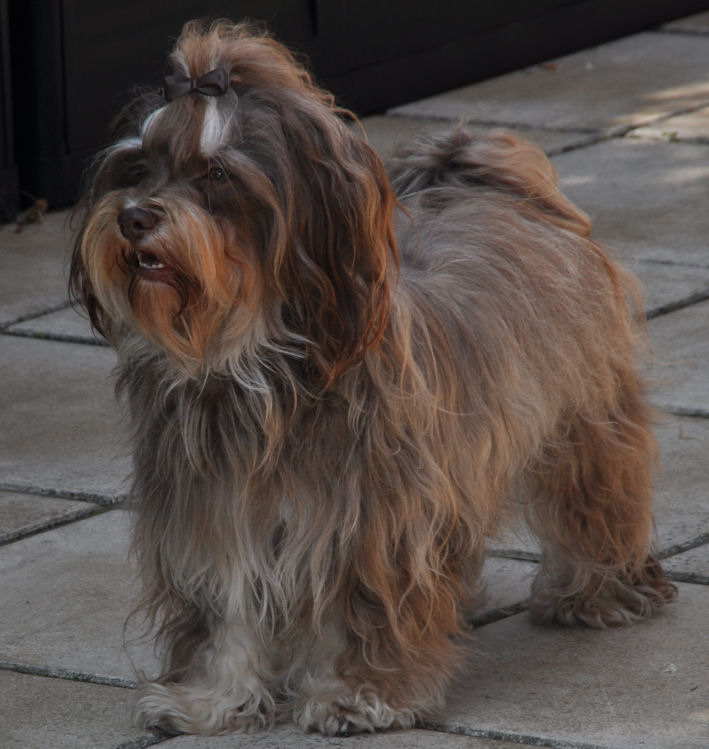
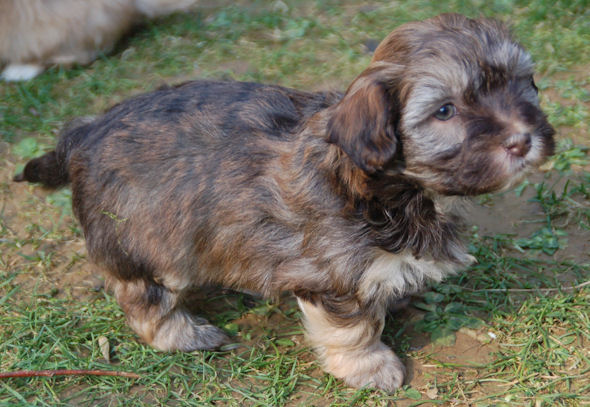
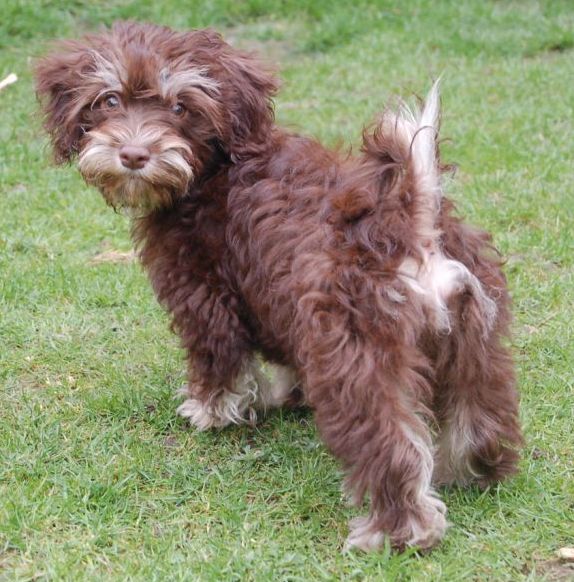
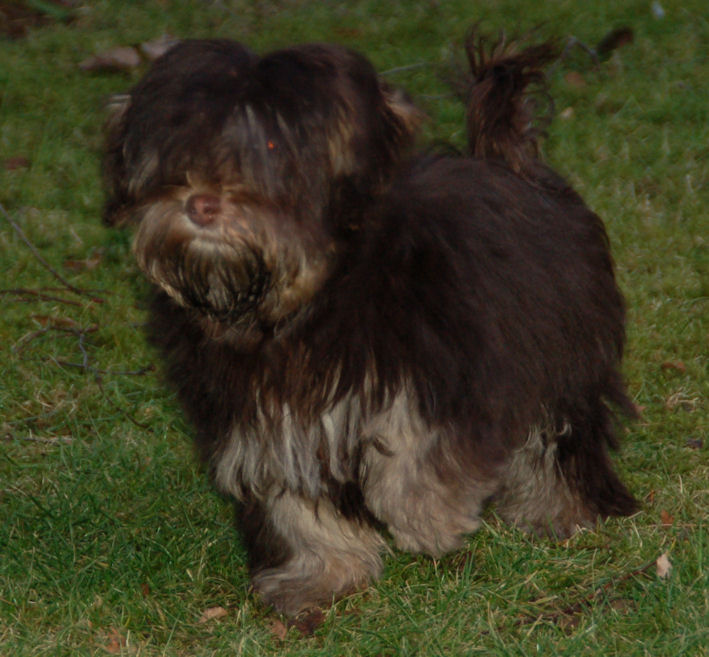
When
two recessive genes meet [bb] and [ee] the
Havanese has a brighter coat colour and a brown
pigment (photo on the left).
The nose can be a bit lighter of colour in
harmony with the lighter coat colour.
CHOCOLATE
is NOT dilution !
In
the Havana Post 31 (August 2008) of the
Havanese Club of the Netherlands an article was
published about the chocolate colour of
Havanese. We would like to give some comments.
(Our thank to
Prof.
Dr. L. Peelman of the University of Ghent)
 The
colour “chocolate”
or brown is
not caused by the pigment pheomelanine (this
causes the yellow-red-orange colours). The
chocolate colour is caused by eumelanine (black
pigment). This black pigment is present in the
“colour cells” in granules. The shape of
these granules determines the colour. If the
granules are elongated the colour is black, if
they are rather round the colour is
brown-chocolate. The quantity of present pigment
doesn’t change and in this sense there is no
dilution. The
colour “chocolate”
or brown is
not caused by the pigment pheomelanine (this
causes the yellow-red-orange colours). The
chocolate colour is caused by eumelanine (black
pigment). This black pigment is present in the
“colour cells” in granules. The shape of
these granules determines the colour. If the
granules are elongated the colour is black, if
they are rather round the colour is
brown-chocolate. The quantity of present pigment
doesn’t change and in this sense there is no
dilution.
A
connexion between the chocolate colour and
immunity failure (immunity problems, skin
irritations, allergies, …) is not demonstrated
in the scientific literature.
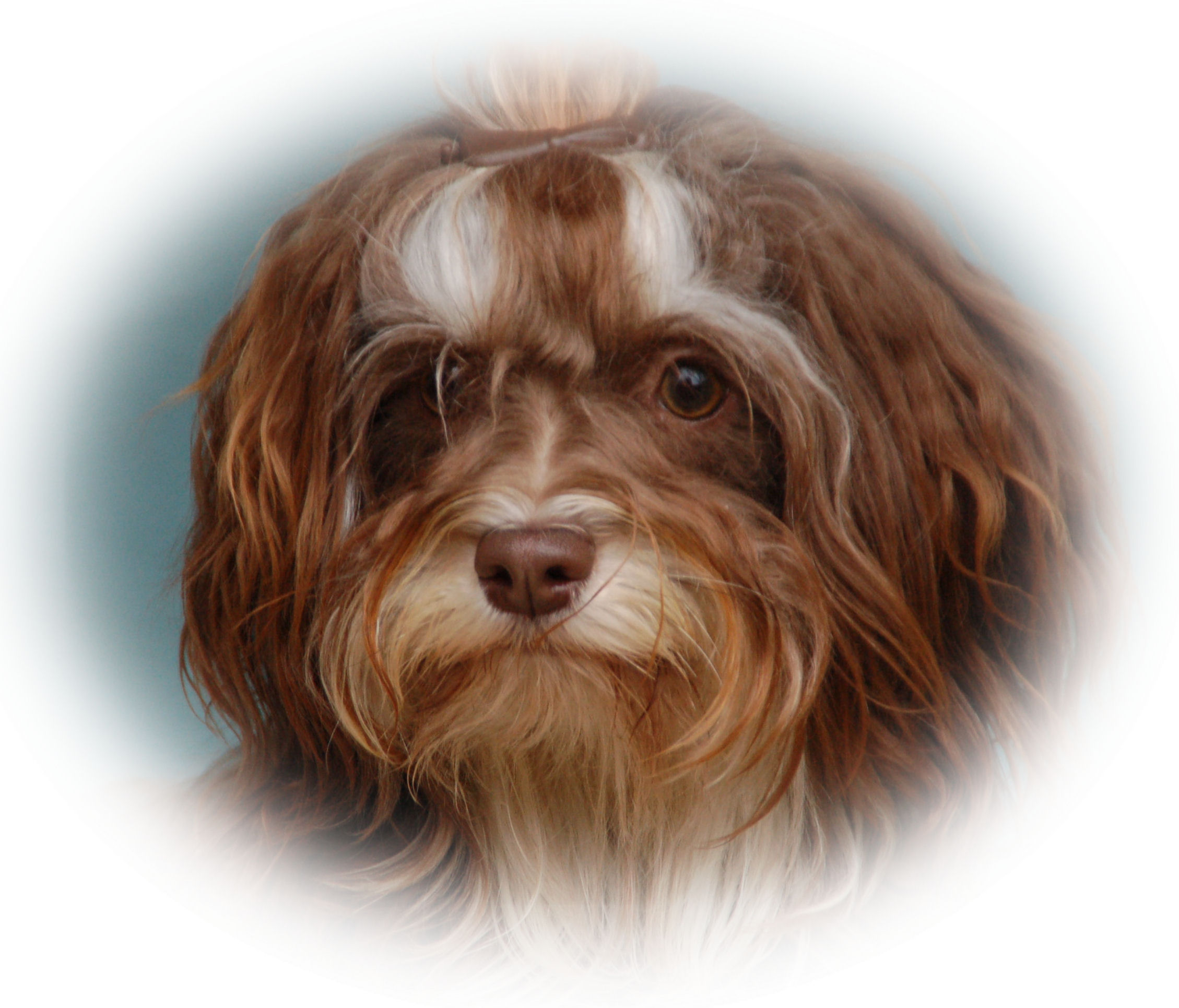
The
colour of the eye of a brown pigmented dog
The
experiences that are often referred to are old
but classic and since than they have never been
contested. Three alleles are recognized on the
locus Ir
(= Iris), in this order of dominance :
Ir+
dark iris (dark brown)
irm
hazel iris (intermediate shade)
iry
yellow iris
 Between
these alleles dominance is not complete, and, as
a consequence, the different possible
combinations correspond with different shades.
To complicate things more, the interference of
modification genes is almost sure. This explains
the continuous series in the gradation, from
pale yellow to dark brown. Between
these alleles dominance is not complete, and, as
a consequence, the different possible
combinations correspond with different shades.
To complicate things more, the interference of
modification genes is almost sure. This explains
the continuous series in the gradation, from
pale yellow to dark brown.
It's
possible to consider the idea that, in general,
the colour of the iris is passed independent of
the coat colour. But some influences of the coat
colour are known :
-
b
makes the iris brighter : with irm
the eyes are light hazel coloured, with iry
very pale yellow. It's useless to search for
very dark iris with a brown coat ;
-
d
dilutes the colour of the eye (« smoky
eyes »).
Source:
Bernard Denis, Génétique
et sélection chez le chien, p. 119 et p.
125
 Colour
of the eyes and nose (pigment) in chocolate Havanese Colour
of the eyes and nose (pigment) in chocolate Havanese
 The
iris is responsible for controlling the amount
of light reaching the retina of the eye and
gives the eye its colour. The iris determines
the way we perceive the colour of the eye. Brown
or green eyes are actually brown or green iris.
Most dogs have dark to gold brown eyes. Dogs
with brown pigment can also have lighter shades
of color. This way hazel, amber and green can
occur. The
iris is responsible for controlling the amount
of light reaching the retina of the eye and
gives the eye its colour. The iris determines
the way we perceive the colour of the eye. Brown
or green eyes are actually brown or green iris.
Most dogs have dark to gold brown eyes. Dogs
with brown pigment can also have lighter shades
of color. This way hazel, amber and green can
occur.
The
colour of the iris is determined by the amount and type
of pigments. The variations in phenotype (perceptible
characteristics) are caused by differences in the
proportion between the two types of
 melanine :
eumelanine and phaeomelanine. melanine :
eumelanine and phaeomelanine.
The
pupil is the opening located in the center of the iris
of the eye that allows light to enter the retina. It
appears black. Influenced by light the pupil can become
larger and smaller.
click
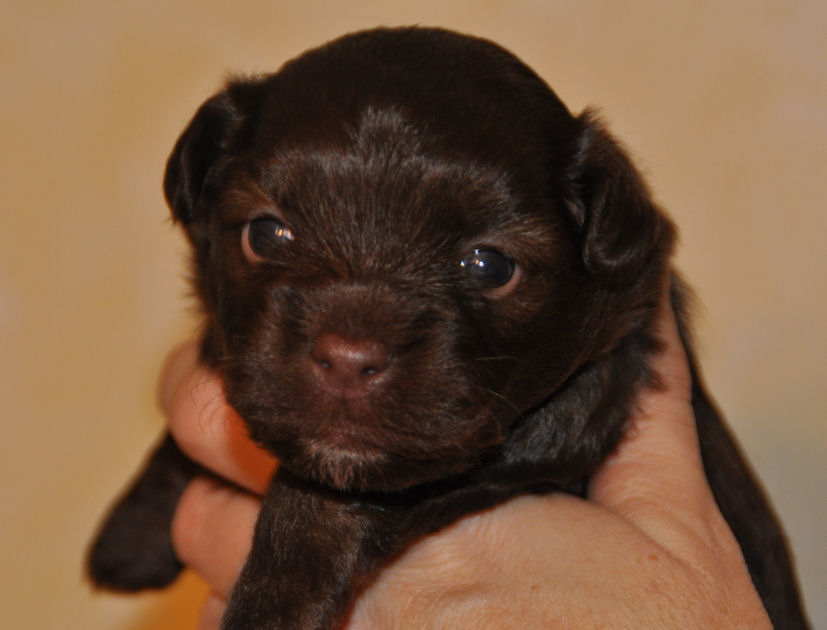
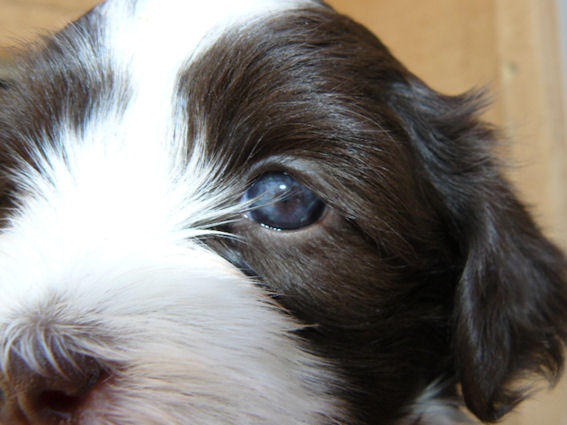
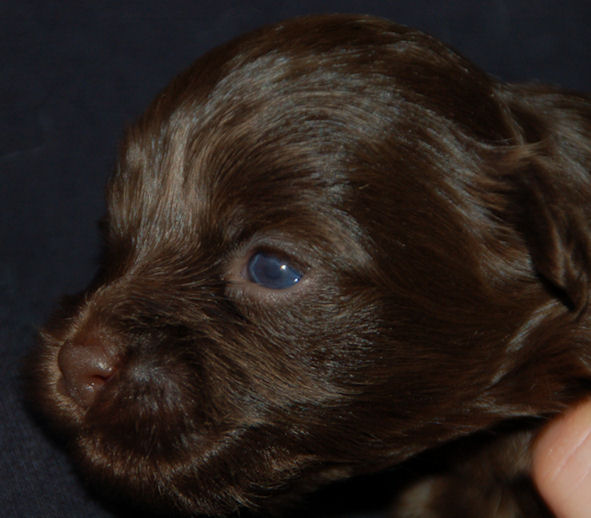
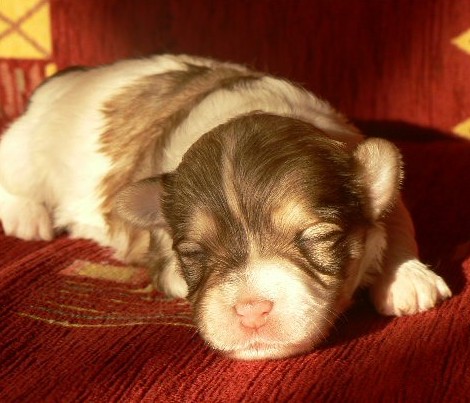
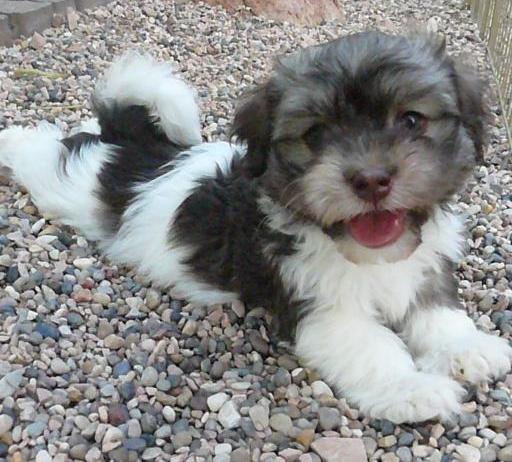
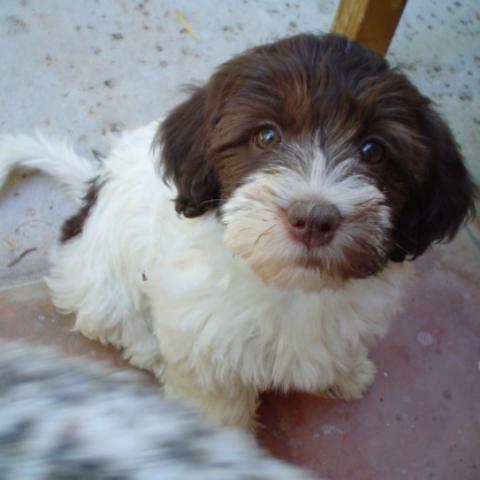
on the pictures to enlarge The
chocolate Havanese puppy has blue
eyes. This can vary from medium to dark blue eyes.
|
eye colour (iris) of chocolate Havanese puppies
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
The
blue iris gradually changes colour. The final colour of the
iris of a chocolate dog can vary from different shades of brown (dark
brown or chestnut brown (also called maroon brown), medium brown, hazel,
light brown or amber)
to different shades of green (dark green, olive green,
medium green, gray green, light green).
Since
chocolate dogs have often lighter iris, they get a very soft
and almost human expression.
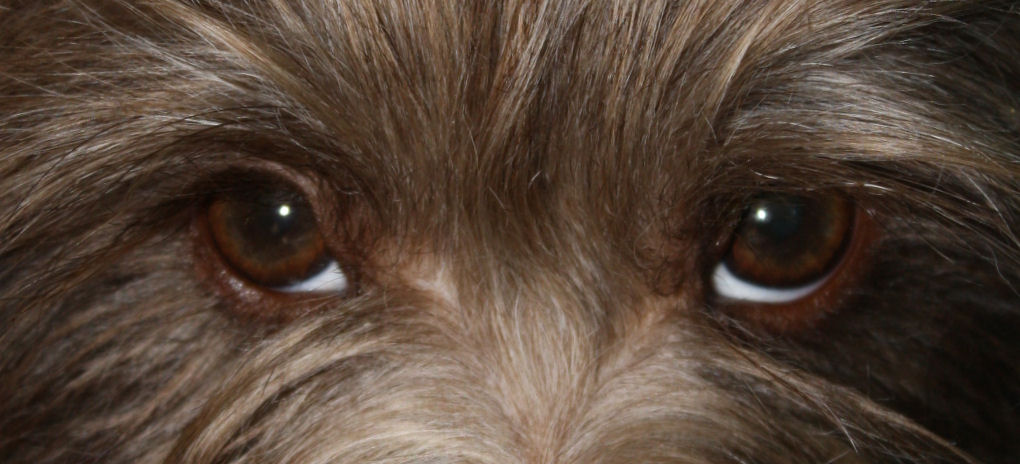
We notice that the inner side of the iris (i.e.
around the pupil) is often darker than the outer part of the
iris (i.e. furthest from the pupil). We observe this in both
black and brown pigmented dogs (see examples). The contrast
can be small, but also relatively big.
If
you look closely (on pictures it's not always easy to see) you
can see that black pigmented dogs have also a darker inner
side of the iris (near the pupil) and a bit lighter outer part
of the iris (furthest
from the pupil). The contrast between the two is
less pronounced than in brown pigmented dogs.
Brown
eyes Most
Havanese eyes are brown. We can observe some different
shades. We propose this classification : °
very dark brown
Most black pigmented Havanese have very dark brown
eyes. They almost appear black. °
dark brown or chestnut brown / maroon brown
Just a little lighter are the dark brown eyes.
Brown eyes often consist of iris with two brown
shades. Thus, the iris can be very dark brown (almost
black) closer to the pupil and dark brown to a kind of
warm reddish brown on the outside. Some of them have a
very small inside part of the iris that is very dark,
the bigger outside part is just regular reddish dark
brown.
Some
have half dark brown, half maroon brown iris. Iris
that consist of two shades of brown can be called
chestnut or marron brown iris. °
medium brown
Medium brown is a shade of brown between dark brown
and light brown. The medium brown iris colour can
occur in combination with a darker shade around the
pupil. °
light brown or amber
Amber
eyes (iris) have a solid colour and a strong golden and russet/coppery tint. It is a warm golden
brown / orange brown eye color.
The light brown iris colour can occur in combination
with darker shades (medium or dark brown) around the
pupil. °
hazel
The
colour hazel is a colour between dark and light brown.
It is a multicoloured iris : dark green (e.g. olive green) or
dark brown around the pupil and medium brown or light brown to
amber on the outside of the iris. Hazel eyes can have small
spots of amber of gold.
The
iris is in fact a combination of two colours : green
and brown. This makes it sometimes difficult to
define the exact eye colour. This can simply be called « hazel
».
A
very common eye colour in chocolate Havanese is hazel. However,
there are different nuances in the dark (around the pupil) and
light colour (outer part) of the iris. Thus, the iris
can be a combination of olive green and medium brown, of olive
green and amber, of medium green and medium brown, etc. The
contrast between both colours (shade of green and brown) in
one iris can be small or big. Green
eyes Green
eyes are not so common. When the iris is a combination
of green with brown we speak of hazel eyes. Some
Havanese have solid green eyes. Some shades of green
are dark green, olive green, medium green, gray green
and light green. Yet it is also possible that the
green colour consists of two shades of green. Just a
bit darker around the pupil (inner side of the iris)
and a bit lighter futher away from the pupil (outer
side of the iris).
Yellow
eyes
Completely
yellow or solid yellow eyes are very common in wolves.
They are rare and undesirable in Havanese. Solid
yellow eyes are also called « prey
eyes »
or « eagle eyes ».
They don't look natural and should not be bred.
Yellow eyes should not be confused with amber
eyes that consist of darker and lighter shade of brown
color.
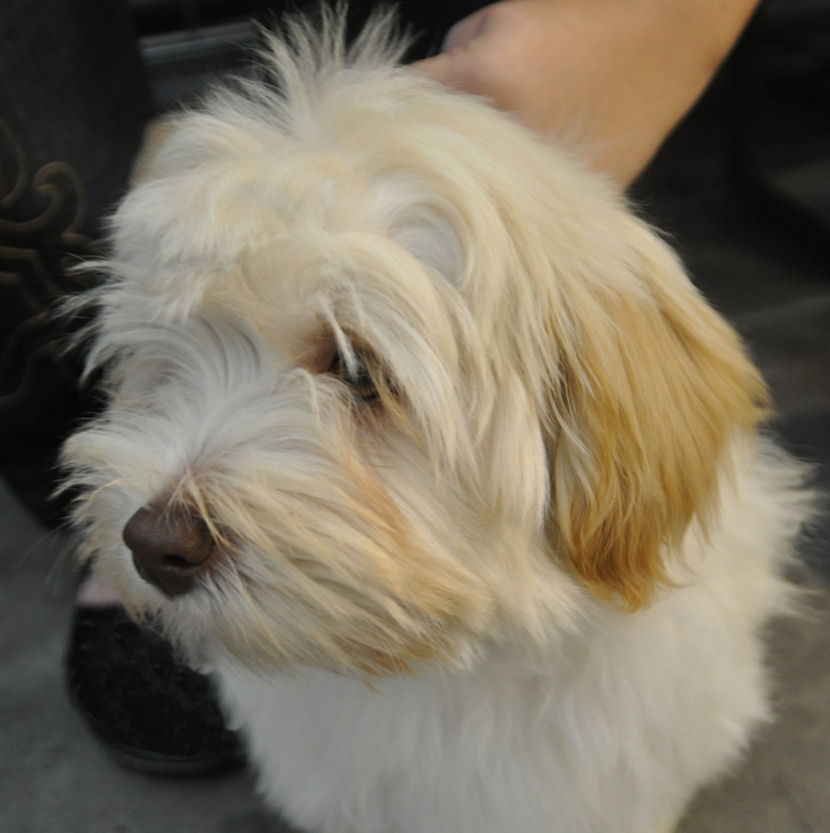
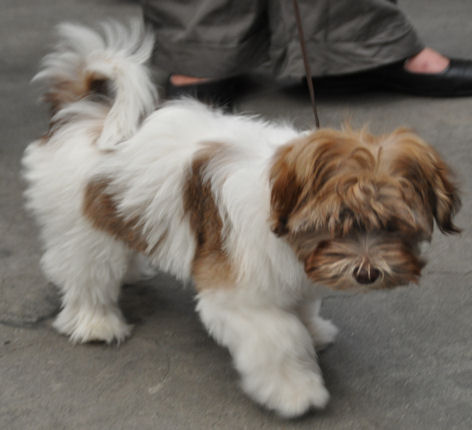
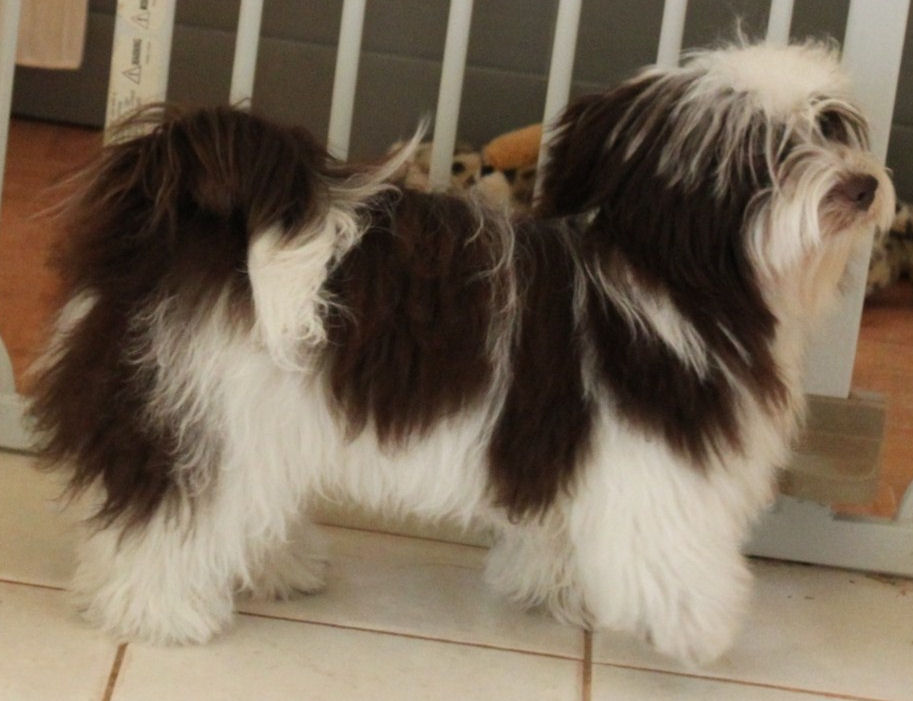
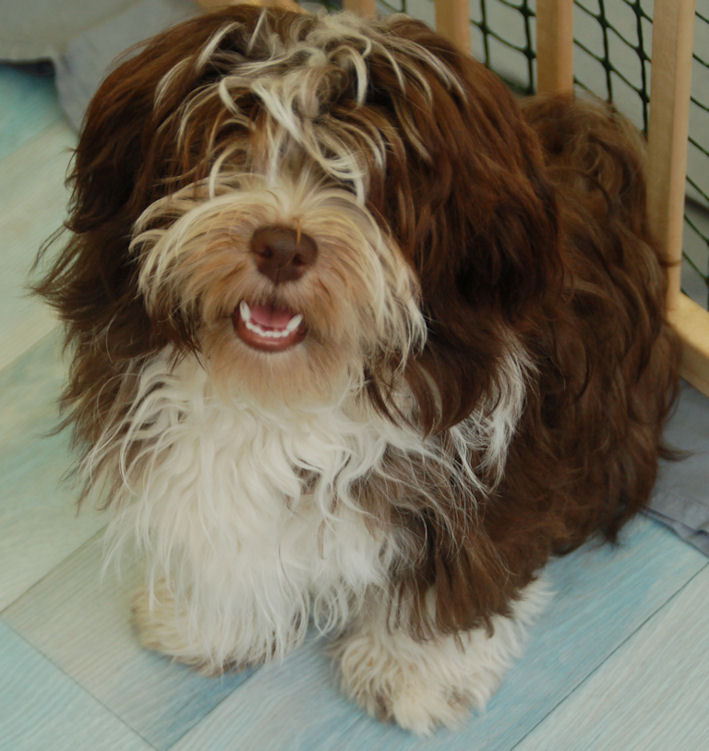
Some examples of eyes and noses of chocolate Havanese:
The colour of the nose of a brown pigmented dog (bb) is brown.
This can vary from dark to light brown.
What
counts for black pigmented dogs, also counts for brown
pigmented dogs: if the coat colour around the nose is white
the pigment of the nose (resp. black or brown) comes in later
on, while the pigment is already present at birth if the coat
colour around the nose is dark (black or brown).
evolution |
|
puppy with white coat around nose |
 |
è
|
 |
| puppy
with dark (brown) coat around nose |
 |
è
|
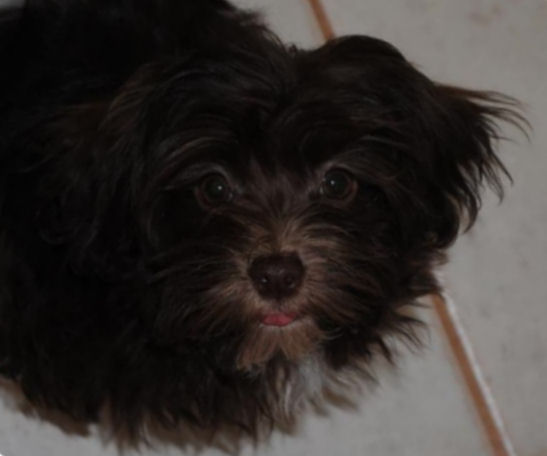 |
puppy with white coat around nose |
puppy with white coat around nose |
|
|
|
puppy with dark (brown) coat around nose |
|
|
|
Chocolate Sable Havanese have generally a bit lighter eyes. Though, their
nose can be very dark.
Remark
Colour perception depends on lighting
conditions!!!
In other words:
eye and nose colour can vary depending on the
light (while taking the picture). In
case that a brown pigmented dog also carries two
dilution genes (bbdd), they have an effect on
both eye (lighter eyes) and nose colour (diluted
brown). It doesn’t often occur in Havanese.
It’s normal though in the Weimaraner breed.
CHOCOLATE
is an ACCEPTED colour
On
the occasion of its meeting end of November 2008
the FCI General Committee approved an
explanatory and summary document titled Breeds
with permitted genetically blue or brown colour as
proposed by the FCI Standards Commission.
Source
 Several
member countries have expressed appreciation
over earlier explanations by Prof. Bernard Denis
about the colour and have asked to have the
breeds with a possibility for genetic blue or
brown colour presented individually. This is the
reason for the following attempt to clarify
again the breeds that can carry the diluted blue
colour and the brown colour. The blue and brown
are not necessarily self-coloured and they can
have tan markings. Several
member countries have expressed appreciation
over earlier explanations by Prof. Bernard Denis
about the colour and have asked to have the
breeds with a possibility for genetic blue or
brown colour presented individually. This is the
reason for the following attempt to clarify
again the breeds that can carry the diluted blue
colour and the brown colour. The blue and brown
are not necessarily self-coloured and they can
have tan markings.
Brown:
(i.e. genetic liver brown, also called
chocolate). Dogs with a genetic brown colour can
never have a black nose and eye colour is
usually hazelnut. The intensity of coat or skin
colour can range from very pale when diluted
(like in Weimaraner) to a deep purple brown
(like in the Deutscher Wachtelhund or the Irish
Water Spaniel).
In breeds where the brown colour occurs, but
where only a black nose is permitted, the
conclusion is that the brown colour is not
accepted in that breed.
Havenese:
GROUP 9 : Brown colour : Bichon Havanais (250)
e.a. Source
Source:
Circular 14/2009 of the FCI published 17/02/2009
Links:
http://www.fci.be/circulaires2009.aspx
http://www.fci.be/circulaires/14-2009.pdf
http://www.fci.be/circulaires/14-2009-annex.pdf
Breeding
with chocolate / brown Havanese
 The
chocolate colour is still very rare in Havanese. This
colour is recessive. This means that both parents must
carry (or show) the brown pigment in order to produce
chocolate coloured puppies. The
chocolate colour is still very rare in Havanese. This
colour is recessive. This means that both parents must
carry (or show) the brown pigment in order to produce
chocolate coloured puppies.
Legenda:
* B = dominant gene : black
* b = recessief gene : brown
* BB = black pigmented dog
* Bb = black pigmented dog, carrier of the brown
pigment
* bb = brown pigmented dog
* black pigmented dog = dog with a black nose, etc.;
the coat can have any colour except chocolate
* brown pigmented dog = dog with a brown nose, etc..;
the coat is mostly chocolate, but can also occur in
other colors, except black
* B and b
= parent 1 (e.g. male)
* B and b
= parent 2 (e.g. female)
* B and b =
descendants (puppies) Possible
combinations : °
If both parents are black pigmented and both do not
carry the brown gene (b), all puppies are black
pigmented (BB).
° If
both parents are black pigmented and only one of them
carries the brown gene (b), all puppies are black
pigmented. In theory 50% of the puppies are carriers
of the brown pigment (Bb).
° If
both parents are black pigmented and both carry the
brown gene (b), in theory 25% of the puppies are brown
pigmented (bb) and in theory 50% of the puppies are
carriers of the brown pigment (Bb).
° If one
parent is brown pigmented (bb) and the other parent is
black pigmented and does not carry the brown gene
(BB), all puppies are black pigmented. All puppies
carry the brown gene (Bb).
° If one
parent is brown pigmented (bb) and the other parent is
black pigmented and carries the brown gene (Bb), in
theory 50% of the puppies are black pigmented and
carry the brown gene (Bb) and in theory 50% of the
puppies are brown pigmented (bb).
° If
both parents are brown pigmented (bb), all puppies are
brown pigmented (bb).
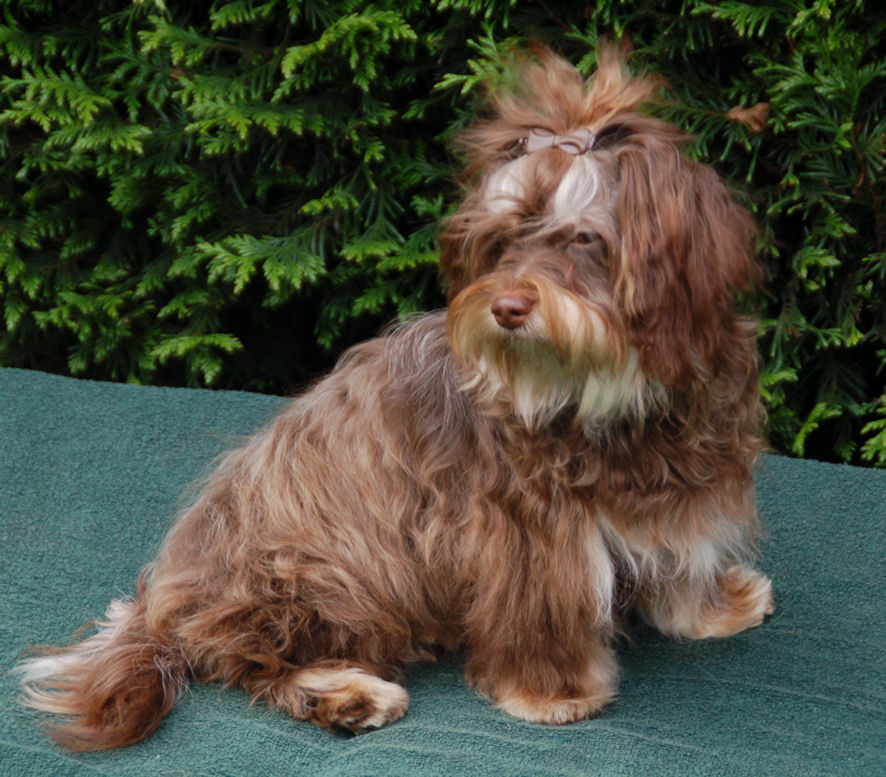
Variations
in Havanese
with the brown pigment
Chocolate
brown coats can vary from dark chocolate to light
chocolate,
from reddish chocolate to grey chocolate. The brown coat colour
can also evolve over time. Thus, dark chocolate can become
reddish chocolate ; dark chocolate can become lighter
cream (cappuccino) and even turn silver.
Chocolate can be the dark colour in the same colour
variations, markings and patterns as black. There are
Chocolate Sable, Chocolate Brindle, Chocolate &
Tan, Chocolate Irish Pied, Chocolate Parti, Chocolate
(Extreme) Piebald Havanese, etc.
The combination of the nose and eye colour is the most
reliable indicator to know whether the dog is really
chocolate, or just has a poor pigmentation, and
therefore is not chocolate. If the dog has dark (black)
eyes and a lighter brown nose, you have a dog with a
poor pigmentation and not a chocolate dog.
Some
examples : Light
coat colours with brown pigment
white with brown pigment |
cream with brown pigment |
red with brown pigment |
 |
 |
 |
| sable
parti + brown pigment |
sable
parti + brown pigment |
cream with brown pigment |
 |
 |
 |
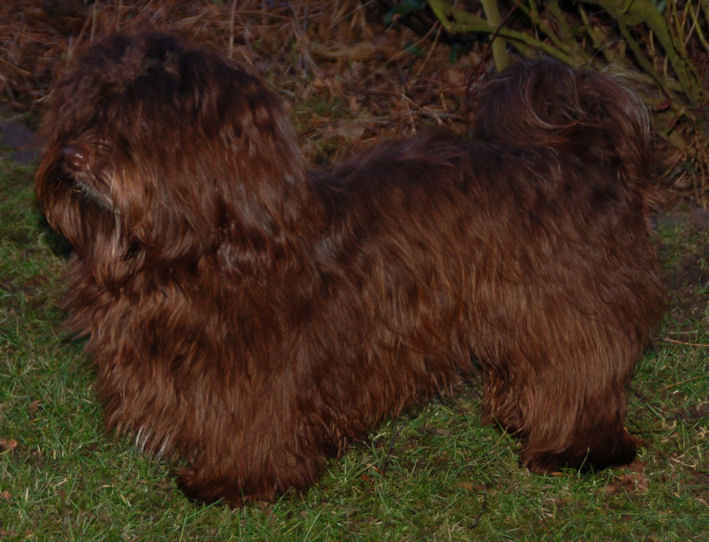
Dark
coat colours with brown pigment
dark chocolate |
light chocolate |
 |
 |
 |
| reddish
chocolate |
grey
chocolate |
 |
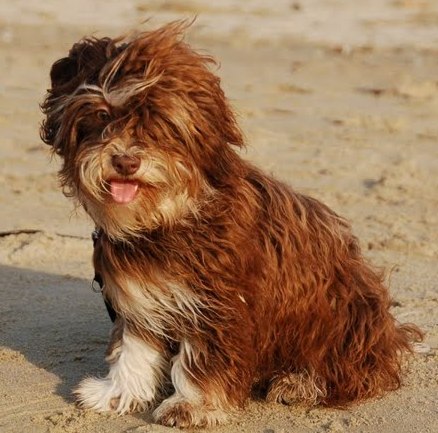 |
 |
Patterns
with brown pigment
| chocolate
brindle |
chocolate
brindle / dark sable |
chocolate
(dark) sable |

(with parti pattern) |

(with irish pied pattern) |
 |
chocolate sable |
chocolate sable |
chocolate sable |

i.e.
"sable" with brown pigment |

(with
parti pattern) |

(with
parti pattern) |
chocolate & tan |
chocolate
& tan |
chocolate
& tan |

chocolate with tan points |

chocolate with tan points |

chocolate with tan points |
Markings
with brown pigment (dark colour = chocolate brown)
| chocolate
extreme piebald |
chocolate piebald |
|

(no
markings on the body) |

(with few
markings on the body) |
|
chocolate parti |
chocolate parti |
chocolate parti |
(lightly
marked parti) |

(lightly
marked parti) |
 |
chocolate parti |
chocolate parti |
chocolate parti |

(heavily
marked parti) |

|

|
chocolate irish pied |
chocolate irish pied |
chocolate irish pied |

(pattern of a Border
Collie) |
 |
 |
chocolate with white markings |
chocolate with white markings |
|
 |
 |
|
Chocolate
Brown versus Havana Brown
There
is some confusion about the names « Chocolate
(Brown) »
and « Havana
Brown ».
Chocolate Brown (dog with brown pigment),
also called « chocolate
»,
« brown
»
or « liver
colour »
(in French « marron
»),
is a name used to define the chocolate / brown
coat colour in dogs. We use the term
chocolate or chocolatebrown because « brown
»
is often used to name a red coat colour (often
sable or brindle with black pigment) which is
not correct.
Havana Brown (dog with black pigment) is
an English term. It's a variation on Brindle :
black, red (or red brown) hairs mixed in the
coat.
The terms « tobacco
colour »
and « reddish
brown »
are
often synonymous with Havana Brown, but they can
also be used to indicate a chocolate coloured
dog. So these terms are subjective.
Note :
HAVANA BROWN comes always with black pigment
(nose, etc.).
ATTENTION : the French name « brun
havane »
is a brown
pigmented dog and with a chocolate brown coat !
Some
examples :
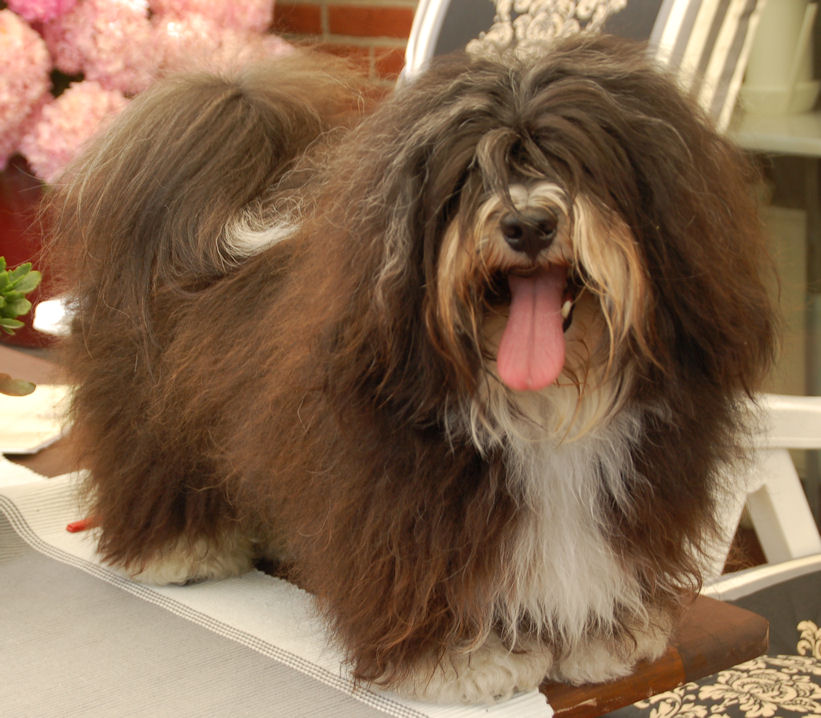
| Chocolate
Brown (brown pigment) |
Havana
Brown (black pigment) |
 |
 |
 |
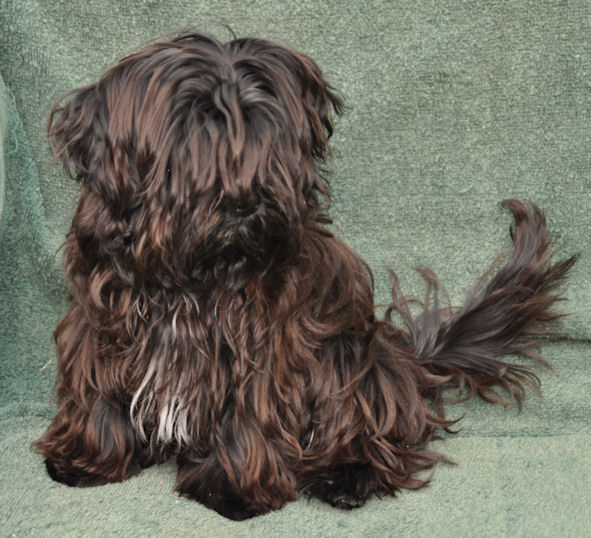 |
| i.e.
= French « brun
havane » |
i.e.
= English « Havana
Brown » |
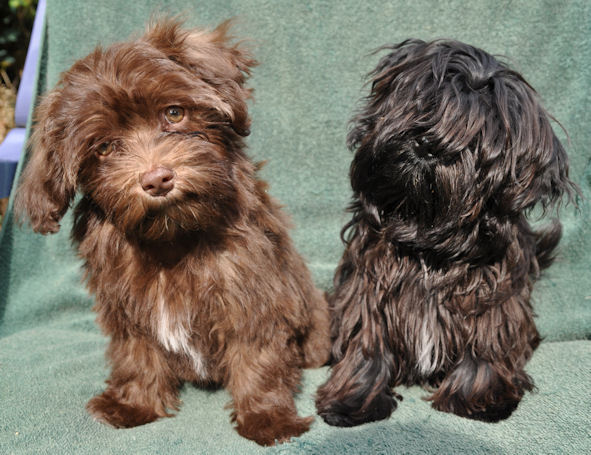
Chocolate Brown vs Havana Brown |
 |
|